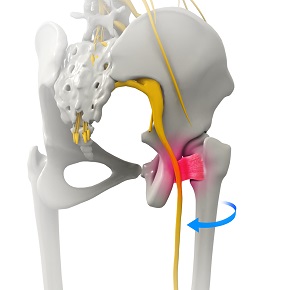
What is Ischiofemoral Impingement Decompression?
Ischiofemoral impingement decompression is a surgery performed to relieve hip pain caused by entrapment or compression of soft tissue in the ischiofermoral space present between the upper part of the thigh bone and the lower back part of the hip bone.
What are the Indications of Ischiofemoral Impingement Decompression?
Athletes or very active individuals who place a lot of stress on their hip joint are likely to suffer from ischiofemoral impingement and may benefit from ischiofemoral impingement decompression. Signs and symptoms include hip pain, presence of edema and inflammation in the ischiofemoral space. A clunking, snapping, or locking sensation of the hip joint may also be reported by patients while walking, running, or taking big steps.
Diagnostic Tests for Ischiofemoral Impingement Decompression
To determine the underlying cause of ischiofemoral impingement, your doctor will review your symptoms and medical history, perform a physical examination, and order certain diagnostic tests.
During the physical examination, your doctor will try to feel for certain weak points in the hips that indicate ischiofemoral impingement. Other diagnostic tests employed include plain radiographs or X-rays, ultrasound studies of the hip and surrounding structures, and MRI.
Treatments for Ischiofemoral Impingement Decompression
Treatments to achieve ischiofemoral impingement decompression include both conservative management and surgical management. If conservative management fails to alleviate symptoms, then surgical option is recommended.
- Conservative management is always the first line of treatment where your doctor recommends physical therapy, activity modification, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, ultrasound, electrical stimulation and shock wave therapy.
- Surgical management involves resection or reshaping of bone and distalization (slightly shifting the position of bone to open up the ischiofemoral space).
Procedure for Ischiofemoral Impingement Decompression
Ischiofemoral impingement decompression can be performed endoscopically or through open surgery. Your surgeon will decide which approach is the best for your condition.
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia with you lying on your back on the operating table. After adequately sterilizing the surgical area, a few small incisions will be made through which the arthroscope and tiny cutting instruments will be inserted. Reshaping of bone will be performed to decompress the impinged tissue. The leg will be moved in various directions to check for satisfactory range of motion. The instruments will then be removed, and the surgical incisions will be closed with absorbable sutures.
Postoperative Care for Ischiofemoral Impingement Decompression
You will be discharged home a day or two after the procedure based on your condition. Limited weight-bearing will be advised by your doctor to facilitate the healing process. Crutches or other assistive devices should be used to aid in walking. Exercises to improve range of motion exercises will be prescribed. Muscle strengthening exercises may be started a week post surgery under your physician’s guidance; however, you should keep away from exercises that aggravate pain and discomfort.










